On the roof: Water stored and evaporated

The risk of flooding in towns and cities is growing as a result of urban sealing and the increase in heavy rain events. The Zinco system build-ups Stormwater Management Roof and the NEW Sponge City Roof can help here.

A standard extensive green roof can store between 20 and 40 l/m² of rainwater. A Stormwater Management Roof or the build-up Sponge City Roof can store a further 55 l/m² or more, depending on the version installed.

Thanks to the Stormwater Management Roof, large volumes of rainwater can also be stored temporarily beneath intensive green roofs with a driveway and photovoltaic unit, and can run off over time.
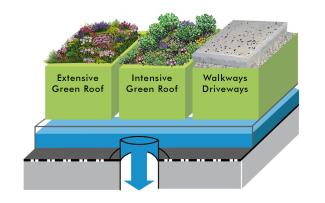
A schematic representation of the basic concept: Rainwater is stored in the storage space beneath the green roof build-up and it runs off through a limiter over time.
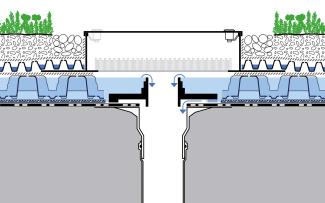
The limiter in the Stormwater Management Roof is placed directly onto the roof waterproof membrane. From the start, it enables the rainwater in the storage space to run off slowly. If more rain falls than can run off, the storage space fills up temporarily and empties again within 24 hours.
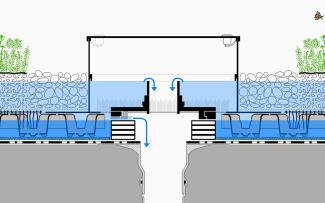
The limiter in the Sponge City Roof is placed onto the dam-up element and only allows the rainwater to run off when this storage space is full. From there, the wicking mat transports the water upwards by capillarity to the substrate layer. If more rain falls during a heavy rain event, it is stored temporarily right into the substrate layer.

Depending on the outlet available – contact flange or screw flange - either Run-Off Limiter set RDS 28 or RDS 48 is used. The water flow rate is set in each case with adjusting rings.

The limiter is protected inside the inspection chamber. The green Spacer RSX 65 of the Stormwater Management Roof can also be seen in the picture.

The fact that the wicking mat transports water upwards from the flood volume by capillarity is what sets the Sponge City Roof with the Run-Off Limiter RS 60 apart. This allows for vegetation to thrive that is particularly species rich.

Approx. 76 l/m² of rainwater can be stored temporarily in the Run-Off Limiter element RSX 80. These spacers are so pressure resistant that you can even drive on them.

With cascade irrigation, excess water is passed on from higher roof areas (building roofs) to lower-lying roof areas (e.g. underground garage roofs) for storage and where applicable for infiltration in a downstream infiltration ditch. © Schmeing Bau GmbH (General contractor), Client: Caja 16 Projekt GmbH, Bocholt
A roof can play a decisive role in the water management of a building, an entire urban district and a city itself provided it is specifically used for its water retention capacity. Temporary water retention on a roof is effective for absorbing heavy rainwater and draining it in a controlled manner and in so doing preventing flooding and the sewerage system from becoming overwhelmed. Additional water storage on a roof is useful for vegetation too, which absorbs and evaporates the available water. As a result, the vegetation becomes more species rich and the surrounding area is cooled. From a technical point of view, Zinco provides various options, from the well-known Stormwater Management Roof to the new system build-up, Sponge City Roof.
Extreme heavy rain events are becoming ever more frequent and are resulting in urban flash floods in our increasingly sealed towns and cities, as the capacity of the existing sewerage system is simply no longer sufficient. It is useful, therefore, to collect the rain and store it temporarily where it actually lands, i.e. on the roof. This is done with the long-standing and well-established Zinco system build-up Stormwater Management Roof. Flat roofs and underground garage roofs lend themselves well as water retention volumes. This is regardless of whether a standard extensive green roof will be growing on the roof or an intensive green roof with walkway, playing surface and driveway, or whether a combined use with photovoltaic is required. In this case, water storage capacity is created beneath the actual green roof build-up using retention spacers. The rainwater is stored in this space and is released over time into the sewerage system or downstream infiltration or water storage systems, using a precisely adjustable run-off limiter.
The loads required for the additional water to be stored and for the increased build-up height should already be taken into account at the planning stage. At the end of the day, the only barrier to this is the concern in people’s minds about standing water on a roof. More than 40 years of experience with intensive green roofs, which have always been reliably installed on 0° roofs, with flood and drain irrigation, show that these concerns are ungrounded. 0° roofs can be planned and executed both in accordance with the Flat Roof Guidelines and DIN 18531, provided a water build-up depth of 100 mm is not exceeded or is exceeded only temporarily. In addition, the “special requirements” relating to the sub-structure (deflection trapezoidal steel sheets) and roof waterproof membrane (e.g. only polymer bituminous sheets instead of bituminous sheets) must be complied with.
Perfect engineering with the Stormwater Management Roof
A Stormwater Management Roof is basically to be designed having regard to local precipitation levels as per the current KOSTRA data, and where applicable, existing discharge limitations. This will provide inflow and outflow volumes that ultimately determine the required height of the water retention space. In order to achieve this dam-up height, Zinco has pressure resistant spacer elements with different heights in its programme. For example, the Retention Spacer RS 60, used primarily under extensive green roofs, is 60 mm high and allows for almost 55 l/m² of additional retained water on the roof. As regards transport and storage, this spacer has the advantage that the elements are stackable and therefore space-saving. In addition, the extremely pressure resistant Retention Spacers RSX 65, 80, 100 and 150 are used beneath an intensive green roof and walkways and driveways. A water retention capacity of up to 142 l/m² is possible in this case. Zinco can offer bespoke solutions where a dam-up level in between or above these levels is required.
From the start, the rainwater runs off over time through the precision adjustable run-off limiter and into the sewerage system or the downstream infiltration or water retention systems. The retention space will fill up if more rain falls than runs off. The exact run-off volume can be set using adjusting rings at the limiter. While the setting chosen is generally such that the retention space is empty again after 24 to 48 hours, other settings are also possible. The maximum flood height is pre-set using infinitely adjustable dam-up pipes. In the event of extreme precipitation events, this allows for excess water to run off where the maximum water level is reached, therefore avoiding structural overload of the roof. The limiter, which is placed directly over the roof outlet, is protected by an inspection chamber. This can be locked, has slots to allow the water to run through and allows for maintenance as part of the maintenance programme that has to be carried out.
Water retention only ever temporary
It should be noted that the additional retention volume of the Stormwater Management Roof has to be adapted to suit anticipated local precipitation events. As a rule, all time intervals (rain duration from 5 minutes to 7 days) taken from what is referred to as the hundred-year rain, which experts now only deem to be a medium-level risk cover, are observed. Based on this, the retention space is designed for the maximum required flood volume. In this way, the spacer will only partly fill up during most rain phases, and that will be the case only until such time as the stored rainwater has completely drained again through the limiter.
Now, it would appear obvious that water stored temporarily during a rain phase should not just be allowed to run off without being used, but that it should be available on the roof for plants. At the same time, this would improve the microclimate due to the greater rate of evaporation. Zinco has developed the new system build-up Sponge City Roof with exactly this in mind. This system provides the ideal combination of accumulated water available for the plants (for good evaporation) and temporary water storage (for protection against flooding).
New system build-up Sponge City Roof
The main technical difference between this innovative system build-up and the Stormwater Management Roof described above is that the lowest point at which water can run off at all into the roof outlet is not directly on the roof waterproof membrane but is higher than that. This height is achieved by fitting one or more 13 mm thick dam-up elements beneath the run-off limiter. During a rain phase, the installed retention spacers now fill up like a fully closed trough up to the level of the limiter element opening. It is only from this level that water can begin to run off into the roof outlet. In this way, a dam is created that serves as a water reservoir for the plants for an extended period of time. If it continues to rain, storage is also possible in the substrate layer of the Sponge City Roof. This situation sounds unusual initially, however, it is expressly approved by the FLL Green Roof Guidelines, provided this accumulated water is only present temporarily in the green roof build-up (quoted from: FLL Green Roof Guidelines Version 2018 p. 59). With the required limiter setting, the retained water generally drains out of the substrate layer again through the limiter, over a period of 24 to 48 hours. This ensures that the plant roots are not damaged from waterlogging.
In contrast, the water remains in the closed tank for a longer period, that is to say, at the level of the retention spacers. In order to have this water available to the plants over a period of time, a wicking mat is installed directly on the retention spacer RS 60, and the wicks dip into the water trough, transporting the water upwards by capillarity to the substrate layer (root area). Thanks to this physical process, the plants have access to additional water, and a plentiful supply of water for a long time during a dry period after the rain event. Nonetheless, the water will be used up at some stage and the retention space empty again. So, this is in fact also a form of temporary water retention that exists periodically depending on the weather and the needs of the plants. The vegetation, dynamically developing between phases of water scarcity and high levels of water, will basically become lush and more species rich than would be the case without this type of flood and drain irrigation. The system build-up Sponge City Roof also has the effect of facilitating the growth of more species rich and insect-friendly extensive green roofs. And, if even greater demands are placed on the vegetation, additional irrigation can be incorporated.
By the way, during the vegetation growth respite in winter, the dam-up elements should be removed for safety reasons, so that an ice layer cannot form on the roof.
Water management of the future
The Stormwater Management Roof and the new system build-up Sponge City Roof are successful examples of how, in the future, concealed technology can be used in building in the background, with the aim of absorbing heavy rain events effectively.
If we consider not only individual roof areas but entire residential districts, commercial or public building complexes in which often courtyards and underground garages are constructed, there is even more potential: Cue - cascade irrigation. Greater structural loads and build-up heights are possible with underground garage roofs, meaning that they can be built without a problem as Stormwater Management Roofs with considerable water retention capacity – all concealed beneath beautiful vegetation and play area and other surfaces. In this way, all the surrounding building roofs can be drained together. Even existing roofs that have no water retention capacity themselves or very little, would pass on rainwater to the water retention level at the underground garage, and over time onto the sewerage system or downstream infiltration system.
The Zinco system build-ups Stormwater Management Roof and Sponge City Roof will take into consideration increasing demands involved in adapting to climate impact, while at the same time increasing the options for water management for an entire site, on and with roofs.
Author: Dipl.-Wirt.-Ing. (FH) Sandra Schöll, Media Office Zinco GmbH
For further information, please contact:
Zinco GmbH
Lise-Meitner-Str. 2
72622 Nuertingen
Germany
Tel. +49 7022 6003-0
e-mail: info@zinco-greenroof.com